Which Is the Best Description of a Strike-slip Fault
Be notified when an answer is posted. 1 as often braided systems of subparallel strike-slip faults defining continental transforms.

Schematic Diagram Of A Primary Dextral Strike Slip Fault And A Download Scientific Diagram
A fault under tension B.

. A left-lateral strike-slip fault is one on which the displacement of the far block is to the left when viewed from either side. Reverse faults occur when one plate slides under the other creating a vertical offset. Strike-slip earthquakes occur along faults that link adjacent segments of the spreading center.
A fault under compression 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement JuanC01 is waiting for your help. What makes a strike slip fault a normal fault. Note that the fault is drawn as the white line in the figure.
Left-lateral fault strike slip fault with little or no friction along fault contact. Note that the fault is. The best description is one that uses vivid words to tell about a person place or thing.
Strike-slip faults are vertical or nearly vertical fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally. Want this question answered. A fault that does not move C.
They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys. Moderate-size normal-fault earthquakes are created at a rift. Large-scale extensional horsetail splays may host sedimentary basins at.
They built it right over a geological fault. The main sense of slip across a strike-slip fault is horizontal. A strike-slip fault is a fault that moves laterally or side to side.
Strike-slip -- Left lateral with no friction. Strike-slip faults are either right-lateral or left-lateral. For the attached figure what is the best description of the fault motion.
Wallace Creek segment of the San Andreas Fault is example of a right-lateral strike-slip fault. Creep Aseismic Slip Imagine a fence across an active fault Slip occurs slowly on the fault continually over time. Megathrust forms along the the plate boundary and creates large earthquakes between the two plates.
A fault that forms at a transform boundary D. A A type of normal fault with a smaller dip b A type of reverse fault with a smaller dip c A type of strike-slip fault with a smaller dip d A fault with no displacement on it. Movements along such a fault may be dextral or sinistral.
Normal faults occur when two plates one on top of the other slide past each other and create the fault. The one in the picture is left-lateral. Creeping faults do not store elastic energy that might be released by a stick-slip event an earthquake.
Strike-slip fault also called transcurrent fault wrench fault or lateral fault in geology a fracture in the rocks of Earths crust in which the rock masses slip past one another parallel to the strike the intersection of a rock surface with the surface or another. Where is the best studied strike slip fault. Which of the following is the best description of a thrust fault.
2On the seismic section the deep strike-slip fault along the S-5 fault zone is characterized by obvious lineups dislocation with locally visible a string of beads strong amplitude Fig. 2 as trench-parallel strike-slip faults contributing to strain partitioning along island and mountain arcs. Antithetic and synthetic splay faults at tips of major strike slip faults have often a small vertical component consistent with the extensional or compressional character of the fault termination.
Up to 10 cash back In the north and middle section the S-5 fault system can be divided into 12 micro-segments mainly distributed in left-stepped oblique-arranged Fig. These faults form when crust pieces slide along each other at a transform plate boundary. Strike-slip fault wrench fault tear fault transcurrent fault A fault in which the major displacement is horizontal and parallel to the strike of a vertical or subvertical fault plane.
Faults that move to the right are called dextral or right-lateral. Continental strike-slip faulting occurs in a range of tectonic environments and patterns. He studied the faulting of the earths crust.
There are three types of faults that may occur in a rock. Normal dip-slip faults are produced by vertical compression as the Earths crust lengthens. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right the slip style is termed right lateral.
The southwestern portion of California is. The San Andreas Fault goes right through California. But the movement can be right lateral ground on opposite side of fault is moving right with respect to the other block or left lateral ground opposite moves left.
While strike-slip faults occur across the world the most famous is the San Andreas fault. B A type of reverse fault with a smaller dip. Strike-slip fault - a geological fault in which one of the adjacent surfaces appears to have moved horizontally faulting geological fault fracture break fault shift - geology a crack in the earths crust resulting from the displacement of one side with respect to the other.
If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the left the motion is termed left lateral. Perhaps the best known is the San Andreas Fault. Faults that move to the left are called sinistral or left.
Which is the best description of a strike-slip fault. Strike-slip faults happen when two plates move horizontally past each other. In strike-slip faulting the rocks slip past each other horizontally.
If the block moves to the left the motion is termed left lateral. That means someone standing near the fault trace and looking across it would see the far side move to the right or to the left respectively. There is no deformation of the rock adjacent to contact.
O reverse faulting O left-lateral strike slip O joint O normal faulting Oright-lateral strike slip. Strike-slip fault - a fault on which the two blocks slide past one another. The hanging wall slides down relative to the footwall.
The San Andreas Fault is an example of a right lateral fault. Add your answer and earn points. In a strike-slip fault the blocks of rock move in opposite horizontal directions.
3 as indent-related strike-slip faults in collisional orogens. Shearing occurs within the accretionary prism. What is the major fault line of California.
Normal fault s are common.

Strike Slip Fault Definition Examples Locations Geology Britannica Slip

Normal Reverse And Strike Slip Faults Youtube

An Interseismic And Coseismic Model For An Ideal Strike Slip Fault Download Scientific Diagram

A Left Lateral Strike Slip Fault Fault Types What Are The Three Main Types Of Faults Geology Page Geology Fault University Of Saskatchewan

Block Diagram Of The Strike Slip Style And Pull Apart Development Download Scientific Diagram

Logic Lineup Earthquake Faults And Plateau Puzzle Normal Reverse Strike Slip Earthquake Fault Plate Tectonic Theory Teamwork Skills
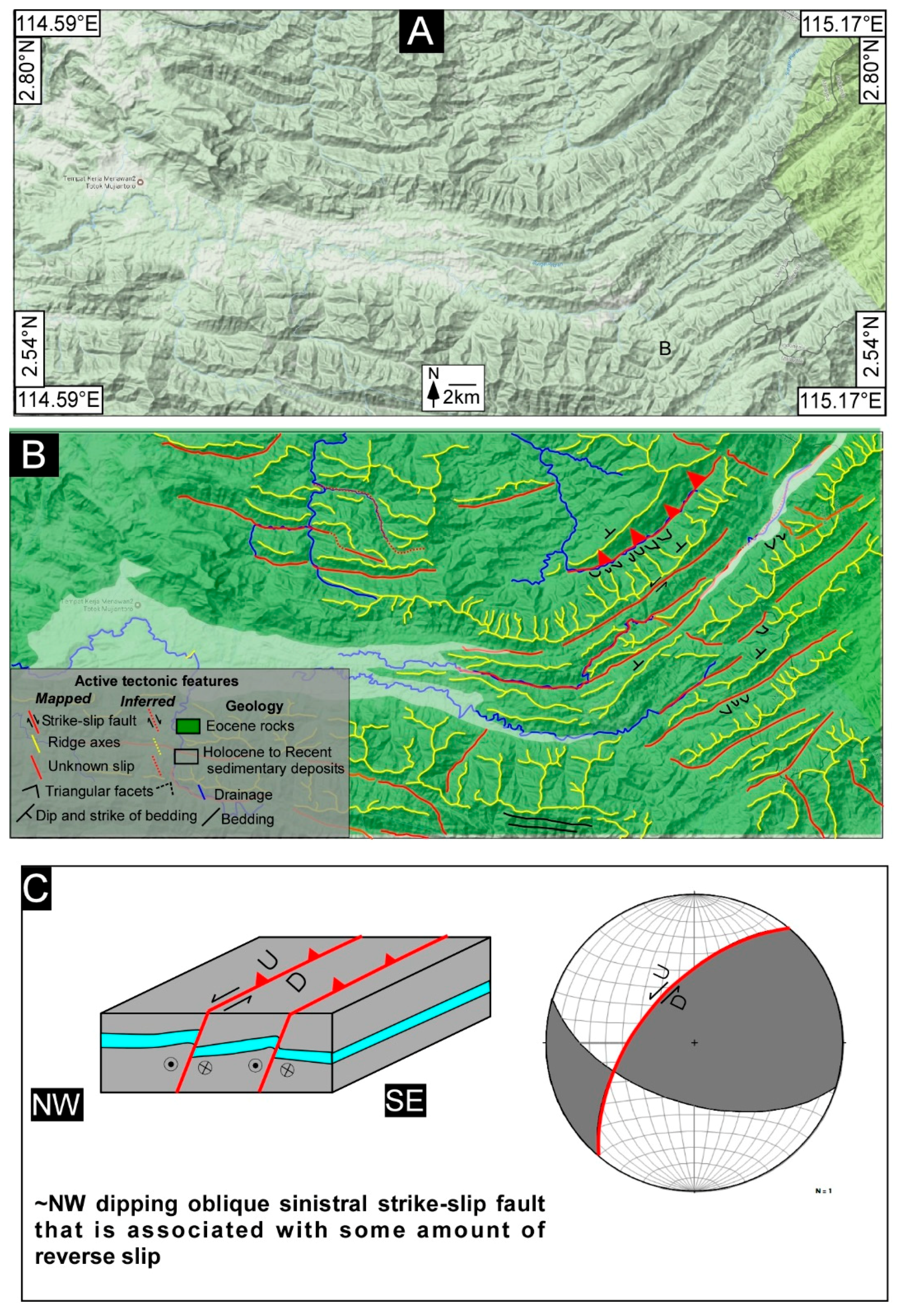
Geosciences Free Full Text Major Strike Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data In Central Borneo Se Asia Html

Tectonic Settings Of Strike Slip Faults And Related Strike Slip Basins Download Scientific Diagram

04 24 Unit X San Andres Fault Flashcards Quizlet

Controls Of A Strike Slip Fault System On The Tectonic Inversion Of The Mahu Depression At The Northwestern Margin Of The Junggar Basin Nw China Sciencedirect

Strike Slip Fault Overview Types What Is A Strike Slip Fault Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
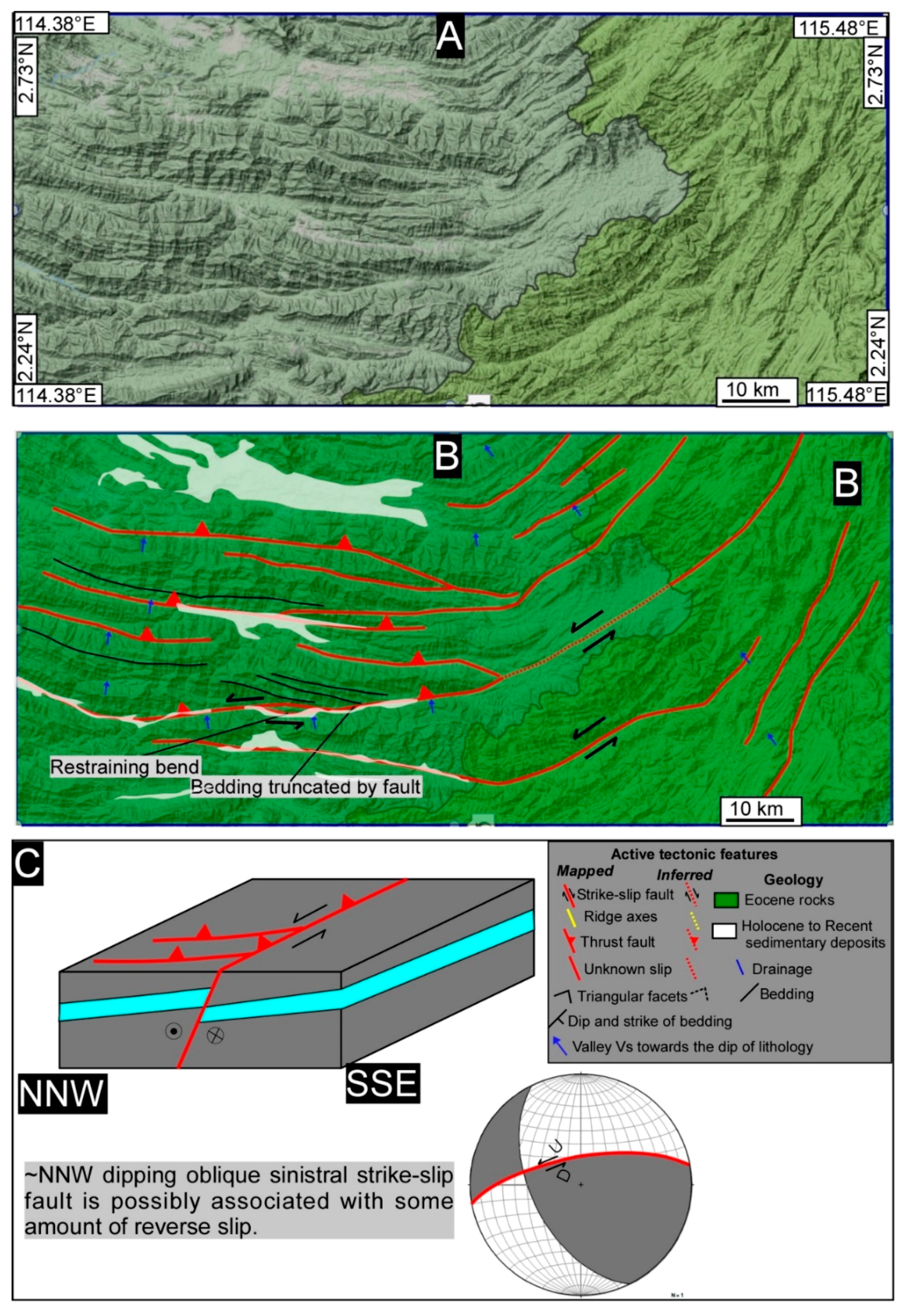
Geosciences Free Full Text Major Strike Slip Faults Identified Using Satellite Data In Central Borneo Se Asia Html

Strike Slip Fault Definition Examples Locations Britannica
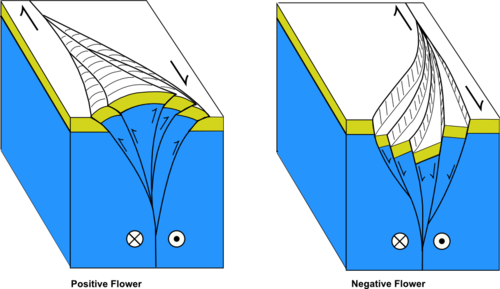
Strike Slip Tectonics Wikiwand

It S Not My Fault Engineering Design Challenge San Andreas Fault Earthquake Engineering

Fault Type Vector Illustration 3 Dimensions Left Lateral Strike Slip Fault Stock Vector Image Art Alamy

The San Andreas Fault Runs For 600 Miles Across California From The Salton Sea Region To The N Coast Beyond Mendocino San Andreas Fault Salton Sea Urban Area

Comments
Post a Comment